CSP Vocab
A list of vocabulary for CSP.
CSP Vocab
Shell Vocab
- pwd: print working directory
- echo: used to display line of text/string that are passed as an argument
- cd: offers way to navigate and change working directory
- ls: lists computer files in Unix and Unix-like operating systems
- env: show setting for your shell
- git clone: sets up a director of files
- cd $project: allows user to move inside that directory of files
- .git: a hidden directory that is used by git to establish relationship between machine and the git server on GitHub
Python Vocab
- string: a sequence of words that are surrounded by quotation marks (they are usually printed)
- variable: a line of code that is defined to complete a certain action
- input: requires input from the user
- output: prints information for the user to see
- function: a group of code that does something
- string concatenation: “+” , which is used to combine strings and variables
- conditional expressions: if, then expressions that require and input or something to be true
Agile Methodology
- Scrum Master: facilitates the sprint by tracking issues and maintaining the scrum board
- DevOps: philosophies, practices, and tools that increases an team’s ability to deliver applications and services at high velocity
- version control, integration, managing dependencies (requirements.txt), AWS deployment are some of the key functions that impact velocity
- Development Team: creates the product
- Frontend: builds the visual part of the website
- Backend: builds the actions and server-type things
- Creativity: ability to fix problems
- Critical Thinking: thinking how to fix the problem
- Communication: helps the team run smoothly without problems in ideas
- Collaboration - Leadership: taking control over certain areas and helping others
- Collaboration - Teamwork: similar to Collaboration with Teamwork
- Researching: helps find solutions to problems
- Technical: making solutions to problems that need solutions
The Internet
- Path: sequence of directly connected computers that send and receive information
- Computer System: a group of computers and programs that work together to do something
- Computer Device: a physical machine that runs a program
- Bandwidth: maximum amount of data that is sent in a fixed amount of time
- Route: process of finding a path from the sender to the receiver
- Computer Network: group of connected computers that are capable of sending/receiving data
Unit 2
- Bits
- a binary digit that is used to store data on a computer
-
010010- each number on here is one bit
- Bytes
- a group of binary digits that operate as a unit
-
0100101- this is a byte, a group of bits
- Hexadecimal
- a numbering system with 16 symbols that can include digits and letters
-
#0000FF- the color blue in hexadecimal
- Nibbles
- 4 binary digits, an 8 bit byte
- these are half a byte
- one hexadecimal digit covers one nibble
- Binary Numbers:
- Unsigned Integer
- integers that don’t have a positive of a negative assigned to them
- always whole numbers and positive
- Signed Integer
- integers that include a positive or negative
- useful in math
- Floating Point
- arithmetic that represents approximate real numbers
- Unsigned Integer
- Binary Data Abstractions:
- Boolean
- a system of algebraic notation that represents a logical action
- ASCII
- American Standard Code for Information Interchange

- the most common character encoding format for text data in computers and on the internet
- American Standard Code for Information Interchange
- Unicode
- information technology standard for the consistent encoding, representation, and handling of text expressed in most of the world’s writing systems
- helps translate between different languages with character ids
- RGB
- hexadecimal values assigned to red, green, and blue
- creates color on computers
- Boolean
- Data Compression:
- Lossy
- the amount of data that is stored in the image is reduced to reduce file size
- this is created from a compressed file back to the original but without perfect resolution
- Lossless
- the reconstructed data is perfectly reconstructed from compressed data
- Lossy
Unit 3
- Variables
- Variables - abstraction that holds value
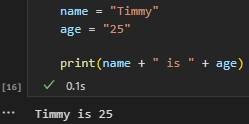
- Variables - abstraction that holds value
- Data Types
- integer - numbers
var a = 1 - string - text/letters
var a = "hello" - boolean - true/false statements
var a = 1 a = True
- integer - numbers
- Assignment Operators
- used to do simple algebra
1 + 2 = a 1 * 2 = a 1 / 2 = a 1 - 2 = a
- used to do simple algebra
- Managing Complexity with Variables:
- Lists
- store multiple elements in a list, allows for more strings to be stored
- lists allow for a lot of data to be stored into one line of code, allowing for cleaner code and less work with creating variables
list = ["a", "b", "c"]
- 2D Lists
- lists with multiple parts, two dimensions
list = [ ["a", "b", "c"], ["a", "b", "c"], ["a", "b", "c"] ]
- lists with multiple parts, two dimensions
- Dictionaries
- store data as values with keys
k, vthisdict = { "brand": "Ford", "model": "Mustang", "year": 1964 }
- store data as values with keys
- Class
- object constructor/blueprint for creating objects ```bash class MyClass: x = 5
p1 = MyClass() print(p1.x) ```
- Lists
- Algorithms
- set of instructions that accomplish a task
- iteration
- selection
- sequencing
def add(): x + y = z print(z)
- set of instructions that accomplish a task
- Sequence
- a list of steps in order to complete a certain task
- Selection
- allows an algorithm to make a decision based on if a condition is met, an example of this is when your car is out of fuel, you go to the gas station to fill your car, but if your car is full you wouldn’t go to the gas station
- if/then statements
if x > 0: print("yes") else: print("no")
- Iteration
- loops of code to complete a certain task
while x == 0 print("0")
- loops of code to complete a certain task
- Expressions
- a way to do math in code
1 + 1 = b print(b) # 2
- a way to do math in code
- Comparison Operators
- compares two values and then outputs an answer
a = 9 b = 5 # Output print(a > b)a = 9 b = 5 # Output print(a != b)
- compares two values and then outputs an answer
- Booleans Expressions and Selection
- uses true/false statements, expressions to compare values and selection with if/then statements to generate an output
a = True if a == True: a = False print("a is false")
- uses true/false statements, expressions to compare values and selection with if/then statements to generate an output
- Booleans Expressions and Iteration
- uses true/false statements, expressions to compare values and loops the comparisons
a = True if a == True: while a == True: print("a is true")
- uses true/false statements, expressions to compare values and loops the comparisons
- Truth Tables
- table for a logical operator containing each variable and all possible input and output results of that operator
- OR: one input must return true
- AND: all inputs must return true
- XOR: only one input can be true
- Characters
- a single letter, number, symbol, or other element
- Strings
- sequence of characters
a = "apple"
- sequence of characters
- Length
- number of characters it contains
a = "apple" print(len(a))
- number of characters it contains
- Concatenation
- combining two or more strings into a single string ```bash a = “apple” b = “banana”
conc = a + b ```
- Upper
- convert a string to all uppercase
a = "apple" print(a.upper())
- convert a string to all uppercase
- Lower
- convert a string to all lowercase ```bash a = “apple” print(a.lower())
- Traversing Strings
- access each character in the string one by one, use a for loop to do this
a = "apple" for x in a: print(x) - index lists
list = ["a", "b"] print(list(1))
- access each character in the string one by one, use a for loop to do this
- Python
- If
- execute a block of code if a specific condition is true
if x > 0: print("a")
- execute a block of code if a specific condition is true
- Elif
- to specify additional conditions to check if the previous conditions are false
if x < 0: print("a") elif x > 1: print("b")
- to specify additional conditions to check if the previous conditions are false
- Else conditionals
- execute a block of code if all of the previous conditions are false
if x < 0: print("a") elif x > 1: print("b") else: print("c")
- execute a block of code if all of the previous conditions are false
- Nested Selection Statements
- control structures that contain other control structures within them
if x > 0: if b > 0: print("c")
- control structures that contain other control structures within them
- For
- used to execute a block of code multiple times
or i in range(1, 10): print(i)
- used to execute a block of code multiple times
- While
- execute a block of code repeatedly until a certain condition is met
x = 0 while x <= 10: print(x) x += 1 - lists
x = [1,2,3] i = 0 while i <= len(x): print(x[i]) i += 1
- execute a block of code repeatedly until a certain condition is met
- If
- Combining loops with conditionals to Break, Continue
- Break: break is used to exit a loop early
- Continue: used to skip the rest of the current iteration and move on to the next one
while y > 0: if x == 0: break if x == 1: continue
- Procedural Abstraction
- abstract away the details of how the task is performed, making your code easier to read and maintain, more efficient code
- Python Def procedures
- how procedures are made with the def word
def func(x): print("a = " + x) func("b")
- how procedures are made with the def word
- Parameters
- values that are passed to the procedure when it is called, defined within the parentheses of the procedure definition
def add(x,y): print(x+y) add(1,2)
- values that are passed to the procedure when it is called, defined within the parentheses of the procedure definition
- Return Values
- value that is returned can be used by the calling code to perform additional tasks or to assign to a variable
def sub(x,y): z = x - y return z print(sub(2,1))
- value that is returned can be used by the calling code to perform additional tasks or to assign to a variable