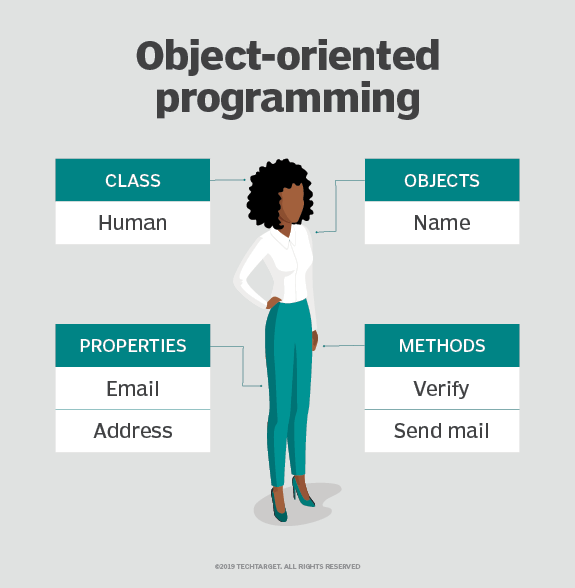
Java
java works with oop (object oriented programming), where objects and classes are made. this method uses classes, objects, methods, and attributes.
Classes
Classes are user-defined data types that are blueprints for each of the objects that are going to be created. They also blueprint how the attributes and methods will behave. These classes can be static or dynamic.
- Static - this sets the class to print out pre-defined variables
- Dynamic - variables can be added to an instance that exists only for the time that the code is run
Below is an example with how a class can be made. This is the same for both dynamic and static classes.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public class HelloStatic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
HelloStatic.main(null); //class is called
|
This is a general way of structuring inside a class.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public class Person
{
// instance variables
// constructors
// methods
}
|
Objects
Objects contain the methods and attributes that are going to be used in the code. They are the instances of the class that is created and are used to house the attributes and methods that are going to be used and executed.
This is how a static class wouldn’t use objects but a dynamic class would.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| // class
public class HelloObject {
private String hello; // instance attribute or variable
public HelloObject() { // constructor
}
public String getHello() { // getter, returns value from inside the object
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloObject ho = new HelloObject(); // object created with variables
System.out.println(ho.getHello());
}
}
|
Methods
Methods are functions defines in a class to describe the behavior of objects. They always start with a reference to an instance object and are reusable.
They are only used in dynamic classes.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public class HelloObject {
private String hello; // instance attribute or variable
public HelloObject() { // constructor
hello = "Hello, World!";
}
public String getHello() { // getter, returns value from inside the object
return this.hello; // return variable from object
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloObject ho = new HelloObject(); // object created with variables (instance of class)
System.out.println(ho.getHello()); // method (gets object)
}
}
HelloObject.main(null);
|
Attributes
These are basically variables in which data is stored. This is where data is taken from when printing it.
Both static and dynamic have attributes.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public class HelloObject {
private String hello; // instance attribute or variable
public HelloObject() { // constructor
hello = "Hello, World!"; // attribute
}
public String getHello() { // getter, returns value from inside the object
return this.hello; // return variable from object
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloObject ho = new HelloObject(); // object created with variables (instance of class)
System.out.println(ho.getHello()); // method (gets object)
}
}
HelloObject.main(null);
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public class HelloStatic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!"); // attribute
}
}
HelloStatic.main(null); //class is called
|
Summary
- Classes - methods that do things (hold all the code)
- Objects - instances that hold data
- Methods - functions that execute something (called by objects)
- Attributes - variables that hold data
Example with Two Constructors
in this example, there are two objects that are created (hd1 and hd2) where each one is called with hellodynamic(), where hd1 is set to the default and hd2 is set to it’s own custom string. both aer defined as variables hello and are then retrieved and printed with the getter method gethello().
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| // Define Class
public class HelloDynamic { // name the first letter of class as capitalized, note camel case
// instance variable have access modifier (private is most common), data type, and name
private String hello;
// constructor signature 1, public and zero arguments, constructors do not have return type
public HelloDynamic() { // 0 argument constructor
this.setHello("Hello, World!"); // using setter with static string
}
// constructor signature, public and one argument
public HelloDynamic(String hello) { // 1 argument constructor
this.setHello(hello); // using setter with local variable passed into constructor
}
// setter/mutator, setter have void return type and a parameter
public void setHello(String hello) { // setter
this.hello = hello; // instance variable on the left, local variable on the right
}
// getter/accessor, getter used to return private instance variable (encapsulated), return type is String
public String getHello() { // getter
return this.hello;
}
// public static void main(String[] args) is signature for main/drivers/tester method
// a driver/tester method is singular or called a class method, it is never part of an object
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloDynamic hd1 = new HelloDynamic(); // no argument constructor
HelloDynamic hd2 = new HelloDynamic("Hello, Nighthawk Coding Society!"); // one argument constructor
System.out.println(hd1.getHello()); // accessing getter
System.out.println(hd2.getHello());
}
}
// IJava activation
HelloDynamic.main(null);
|
1
2
| Hello, World!
Hello, Nighthawk Coding Society!
|
Hacks
These are my Java hacks.
Java Hello
in here i attempted to build a database with a dynamic class, which i managed to do successfully by creating the data and then printing it and editing it. i also attempted to build an sqlite data base with a .jar file with the magic commands that jupyter uses, however i wasn’t able to do this because there were issues importing the sqlite-jdbc-3.36.0.3.jar in order to build the data table.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
| // imports libraries for sqlite
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Scanner;
// attempt at importing a .jar file to get data into sqlite
// %jars /sqlite-jdbc-3.36.0.3.jar
// class for person
class Person {
// signature makes these variables private to class
private String name; // attribute
private int age;
private int height;
private int weight;
public Person(String name, int age, int height, int weight) { // constructor to initialize the person attributes
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
}
// these are public, making them accessible to everywhere
// void checks for correct input
// setter methods
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setHeight(int height) {
this.height = height;
}
public void setWeight(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
//display method for data (getter)
public void display() {
System.out.println("Name: " + name);
System.out.println("Age: " + age + " years");
System.out.println("Height: " + height + " centimeters");
System.out.println("Weight: " + weight + " kilograms");
}
}
// class for food
class Food {
private String type; // attribute
private double cost;
private int calories;
private int protein;
private int sugar;
public Food(String type, double cost, int calories, int protein, int sugar) { // constructor to initialize the food attributes
this.type = type;
this.cost = cost;
this.calories = calories;
this.protein = protein;
this.sugar = sugar;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public void setCost(double cost) {
this.cost = cost;
}
public void setCalories(int calories) {
this.calories = calories;
}
public void setProtein(int protein) {
this.protein = protein;
}
public void setSugar(int sugar) {
this.sugar = sugar;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Type: " + type);
System.out.println("Cost: $" + cost);
System.out.println("Calories: " + calories);
System.out.println("Protein: " + protein + " grams");
System.out.println("Sugar: " + sugar + " grams");
}
}
// class for location
class Location {
private String city; // attribute
private String state;
private String zip;
public Location(String city, String state, String zip) { // constructor to initialize the location attributes
this.city = city;
this.state = state;
this.zip = zip;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
public void setZip(String zip) {
this.zip = zip;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("City: " + city);
System.out.println("State: " + state);
System.out.println("Zip Code: " + zip);
}
}
// class for grouping all the classes into one
class Group {
public Person person; // attribute that are classes
public Food food;
public Location location;
public Group(Person person, Food food, Location location) { // constructor to initialize the class attributes
this.person = person;
this.food = food;
this.location = location;
}
public void displayGroupInfo() {
System.out.println("Person Info:");
person.display();
System.out.println("\nFood Info:");
food.display();
System.out.println("\nLocation Info:");
location.display();
}
// chatGPT sqlite attempt
public void createSQLiteTable() {
// SQLite database file path
String dbFilePath = "/instances/database.db";
// SQL statement to create the table
String createTableSQL = "CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS GroupInfo ("
+ "personName TEXT, personAge INT, personHeight INT, personWeight INT,"
+ "foodType TEXT, foodCost REAL, foodCalories INT, foodProtein INT, foodSugar INT,"
+ "city TEXT, state TEXT, zip TEXT)";
// Establish connection and execute SQL statement
try (Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:sqlite:" + dbFilePath);
Statement statement = connection.createStatement()) {
// Create the table
statement.executeUpdate(createTableSQL);
System.out.println("SQLite table created successfully.");
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.err.println("Error creating SQLite table: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
public class MainDynamic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// allows for user input
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
//print statements for user input
System.out.print("Enter person name: ");
String personName = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.print("\nEnter person age: ");
int personAge = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("\nEnter person height: ");
int personHeight = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("\nEnter person weight: ");
int personWeight = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine();
System.out.print("\nEnter food: ");
String foodType = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.print("\nEnter food cost: ");
double foodCost = scanner.nextDouble();
System.out.print("\nEnter food calories: ");
int foodCalories = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("\nEnter food protein: ");
int foodProtein = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("\nEnter food sugar: ");
int foodSugar = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine();
System.out.print("\nEnter city: ");
String city = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.print("\nEnter state: ");
String state = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.print("\nEnter ZIP code: ");
String zip = scanner.nextLine();
scanner.nextLine();
// gathering all information from scanner into objects
Person person = new Person(personName, personAge, personHeight, personWeight);
Food food = new Food(foodType, foodCost, foodCalories, foodProtein, foodSugar);
Location location = new Location(city, state, zip);
// gathering all data from classes into one
Group group = new Group(person, food, location);
// printing initial data
System.out.println();
System.out.println("\nGroup Info:");
group.displayGroupInfo();
scanner.close(); // stopping inputs
group.createSQLiteTable(); // making sqlite table
// updating data in the database
group.person.setName("David");
group.person.setHeight(196);
group.food.setCost(63.28);
group.location.setCity("Los Angeles");
// printing new data
System.out.println();
System.out.println("\nGroup Info:");
group.displayGroupInfo();
}
}
// running program
MainDynamic.main(null);
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
| Enter person name:
Enter person age:
Enter person height:
Enter person weight:
Enter food:
Enter food cost:
Enter food calories:
Enter food protein:
Enter food sugar:
Enter city:
Enter state:
Enter ZIP code:
Group Info:
Person Info:
Name: Bob
Age: 56 years
Height: 257 centimeters
Weight: 45 kilograms
Food Info:
Type: Cake
Cost: $25.0
Calories: 304
Protein: 2 grams
Sugar: 79 grams
Location Info:
City: San Diego
State: CA
Zip Code: 92127
Error creating SQLite table: No suitable driver found for jdbc:sqlite:/instances/database.db
Group Info:
Person Info:
Name: David
Age: 56 years
Height: 196 centimeters
Weight: 45 kilograms
Food Info:
Type: Cake
Cost: $63.28
Calories: 304
Protein: 2 grams
Sugar: 79 grams
Location Info:
City: Los Angeles
State: CA
Zip Code: 92127
|
Java Console Game
In here, I modified the Tic Tac Toe game to make it more efficient.
i started with making the main game class. instead of creating the board with an array, i made it by counting to 9 with a loop. this is more efficient than typing out each number. after that i made the symbols in an array and i also make the quit variable so that the game runs. in this section i cover unit 1 (using java components), unit 2 (using objects), unit 3 (booleans) unit 4 (iteration), unit 5 (classes), unit 6 (array with players), unit 8 (2d array), unit 10 (recursion with building board). recognizing the collegeboard units is important because it shows if i know the information needed for the ap exam. rebuilding the program helps me learn the structure of the code better.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| import java.util.Scanner;
public class TicTacToeGame {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Tic Tac Toe");
Scanner scTTT = new Scanner(System.in);
String[] board = new String[9]; // board is made without array, instead by counting
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
board[i] = String.valueOf(i + 1); // creates initial board
}
String[] players = {"X", "O"}; // symbols
boolean quit = false; // makes game run
System.out.println("Type the number of the square you want to place your piece in");
int currentPlayer = 0;
int turn = 0;
// while loop later
scTTT.close();
}
// ...other classes below
}
|
Game Logic
I then use a loop to run through the turns, each turn stating which players turn it is and placing valid turns only. Turns that are out of the range of the numbers on the board or if the spot is already taken, the game won’t continue. If the turn is valid, then the turn will be placed and the game continues. The game also checks if there’s a win, which is another class, however if there is a win then the player is notified or if there is a tie the player is also notified.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| while (!quit) {
System.out.println("Player " + (currentPlayer + 1) + "'s turn (" + players[currentPlayer] + ")");
printBoard(board); // prints current board (with moves)
int move = scTTT.nextInt() - 1;
if (move < 0 || move >= board.length || !board[move].equals(String.valueOf(move + 1))) {
System.out.println("Invalid move, try again.");
continue; // tests if move is valid (if it's on open spot)
}
board[move] = players[currentPlayer]; // places turn on board
turn++;
if (checkWin(board, players[currentPlayer])) { // checks if player wins
System.out.println("Player " + (currentPlayer + 1) + " wins!");
quit = true; // if one player wins (3 in a row), player wins
} else if (turn == 9) {
System.out.println("It's a tie!");
quit = true; // if it's a tie (all blocks are filled), game ends
}
currentPlayer = (currentPlayer + 1) % 2; // moves to next turn
}
|
Printing Board
in order to print the board i have a loop that prints the rows, where i is the number of times we loop through in order to get the proper columns.
1
2
3
4
5
| public static void printBoard(String[] board) {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i += 3) {
System.out.println(board[i] + " | " + board[i + 1] + " | " + board[i + 2]); // prints board
}
}
|
Checking for Wins
in order to check for wins we have arrays that are predefined to show what winning patterns look like. the program then checks to see if there are any patterns that match and if there are, true is returned, signaling that the game is over and that one of the platers won.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public static boolean checkWin(String[] board, String player) {
// using arrays for game board
int[][] winPatterns = {
{0, 1, 2}, {3, 4, 5}, {6, 7, 8}, // rows
{0, 3, 6}, {1, 4, 7}, {2, 5, 8}, // columns
{0, 4, 8}, {2, 4, 6} // diagonals
};
for (int[] pattern : winPatterns) {
if (board[pattern[0]].equals(player) && board[pattern[1]].equals(player) && board[pattern[2]].equals(player)) {
return true; // check for win (based on win patterns above)
}
}
return false; // no win
}
|
This is the fully running game.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
| import java.util.Scanner;
public class TicTacToeGame {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Tic Tac Toe");
Scanner scTTT = new Scanner(System.in);
String[] board = new String[9]; // board is made without array, instead by counting
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
board[i] = String.valueOf(i + 1); // creates initial board
}
String[] players = {"X", "O"}; // symbols
boolean quit = false; // makes game run
System.out.println("Type the number of the square you want to place your piece in");
int currentPlayer = 0;
int turn = 0;
while (!quit) {
System.out.println("Player " + (currentPlayer + 1) + "'s turn (" + players[currentPlayer] + ")");
printBoard(board); // prints current board (with moves)
int move = scTTT.nextInt() - 1;
scTTT.nextLine(); // Consume the newline character
if (move < 0 || move >= board.length || !board[move].equals(String.valueOf(move + 1))) {
System.out.println("Invalid move, try again.");
continue; // tests if move is valid (if it's on open spot)
}
board[move] = players[currentPlayer]; // places turn on board
turn++;
if (checkWin(board, players[currentPlayer])) { // checks if player wins
System.out.println("Player " + (currentPlayer + 1) + " wins!");
quit = true; // if one player wins (3 in a row), player wins
} else if (turn == 9) {
System.out.println("It's a tie!");
quit = true; // if it's a tie (all blocks are filled), game ends
}
currentPlayer = (currentPlayer + 1) % 2; // moves to next turn
}
scTTT.close();
}
public static void printBoard(String[] board) {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i += 3) {
System.out.println(board[i] + " | " + board[i + 1] + " | " + board[i + 2]); // prints board
}
}
public static boolean checkWin(String[] board, String player) {
// using arrays for game board
int[][] winPatterns = {
{0, 1, 2}, {3, 4, 5}, {6, 7, 8}, // rows
{0, 3, 6}, {1, 4, 7}, {2, 5, 8}, // columns
{0, 4, 8}, {2, 4, 6} // diagonals
};
for (int[] pattern : winPatterns) {
if (board[pattern[0]].equals(player) && board[pattern[1]].equals(player) && board[pattern[2]].equals(player)) {
return true; // check for win (based on win patterns above)
}
}
return false; // no win
}
}
TicTacToeGame.main(null)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| Tic Tac Toe
Type the number of the square you want to place your piece in
Player 1's turn (X)
1 | 2 | 3
4 | 5 | 6
7 | 8 | 9
Player 2's turn (O)
X | 2 | 3
4 | 5 | 6
7 | 8 | 9
Player 1's turn (X)
X | 2 | O
4 | 5 | 6
7 | 8 | 9
Player 2's turn (O)
X | X | O
4 | 5 | 6
7 | 8 | 9
Player 1's turn (X)
X | X | O
4 | 5 | 6
7 | 8 | O
Player 2's turn (O)
X | X | O
4 | 5 | 6
7 | X | O
Player 1's turn (X)
X | X | O
4 | 5 | 6
O | X | O
Player 1 wins!
|
Other Games
Below are the other two games remade.
Higher Or Lower
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class HLGame {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
Random random = new Random();
int correctNum = random.nextInt(10) + 1;
int attempts = 0;
System.out.println("What number am I thinking of (1-10)?");
while (true) {
System.out.print("Guess: ");
int attemptNum = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println(attemptNum);
attempts++;
if (attemptNum < correctNum) {
System.out.println("higher");
} else if (attemptNum > correctNum) {
System.out.println("lower");
} else {
System.out.println("Correct!");
break;
}
}
scanner.close();
}
}
HLGame.main(null)
|
1
2
3
4
5
| What number am I thinking of (1-10)?
Guess: 5
higher
Guess: 7
Correct!
|
Rock Paper Scissors
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class RPSGame {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
Random random = new Random();
System.out.println("Choose: 1 - Rock, 2 - Paper, 3 - Scissors");
int pChoice = scanner.nextInt();
int cChoice = random.nextInt(3) + 1;
String[] choices = {"Rock", "Paper", "Scissors"};
System.out.println("Computer: " + choices[cChoice - 1]);
System.out.println("Player: " + choices[pChoice - 1]);
int result = (pChoice - cChoice + 3) % 3;
if (result == 0) {
System.out.println("Tie");
} else if (result == 1) {
System.out.println("You win");
} else {
System.out.println("You lose");
}
scanner.close();
}
}
RPSGame.main(null)
|
1
2
3
4
| Choose: 1 - Rock, 2 - Paper, 3 - Scissors
Computer: Paper
Player: Rock
You lose
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
| import java.util.Scanner;
import java.lang.Math;
import java.util.Random;
public class ConsoleGame {
public final String DEFAULT = "\u001B[0m"; // Default Terminal Color
public void start() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Welcome to the Console Game!");
boolean quit = false;
while (!quit) {
menuString();
try {
int choice = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(choice + ": ");
if (choice == 0) {
System.out.println("Goodbye, World!");
quit = true;
} else {
quit = action(choice);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
sc.nextLine();
System.out.println(e + ": Not a valid choice, try again.");
}
}
sc.close();
}
public void menuString(){
String menuText = ""
+ "\u001B[38;5;141m___________________________\n"
+ "|~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~|\n"
+ "|\u001B[0m Menu! \u001B[38;5;141m|\n"
+ "|~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~|\n"
+ "| 0 - Exit |\n"
+ "| 1 - Rock Paper Scissors |\n"
+ "| 2 - Higher or Lower |\n"
+ "| 3 - Tic Tac Toe |\n"
+ "|_________________________| \u001B[0m\n"
+ "\n"
+ "Choose an option.\n";
System.out.print(menuText);
}
private boolean action(int selection) {
boolean quit = false;
switch (selection) {
case 1:
rps();
break;
case 2:
horl();
break;
case 3:
ticTacToe();
break;
default:
System.out.println("Unexpected choice, try again.");
}
System.out.println(DEFAULT);
return quit;
}
public void rps() {
Scanner scRPS = new Scanner(System.in);
Random random = new Random();
System.out.println("Choose: 1 - Rock, 2 - Paper, 3 - Scissors");
int pChoice = scRPS.nextInt();
int cChoice = random.nextInt(3) + 1;
String[] choices = {"Rock", "Paper", "Scissors"};
System.out.println("Computer: " + choices[cChoice - 1]);
System.out.println("Player: " + choices[pChoice - 1]);
int result = (pChoice - cChoice + 3) % 3;
if (result == 0) {
System.out.println("Tie");
} else if (result == 1) {
System.out.println("You win");
} else {
System.out.println("You lose");
}
scRPS.close();
}
public void horl() {
Scanner scHRL = new Scanner(System.in);
Random random = new Random();
int correctNum = random.nextInt(10) + 1;
int attempts = 0;
System.out.println("What number am I thinking of (1-10)?");
while (true) {
System.out.print("Guess: ");
int attemptNum = scHRL.nextInt();
System.out.println(attemptNum);
attempts++;
if (attemptNum < correctNum) {
System.out.println("higher");
} else if (attemptNum > correctNum) {
System.out.println("lower");
} else {
System.out.println("Correct!");
break;
}
}
scHRL.close();
}
//player variables
private static final String PLAYER_X = "X";
private static final String PLAYER_O = "O";
public void ticTacToe() {
System.out.println("Tic Tac Toe");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
Random random = new Random();
// setting board length
String[] board = new String[9];
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
board[i] = String.valueOf(i + 1);
}
String[] players = {PLAYER_X, PLAYER_O};
boolean quit = false;
// choosing game mode
System.out.println("Choose game mode: ");
System.out.println("1. Play against player");
System.out.println("2. Play against computer");
// sets gamemode
int gameMode = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine();
int currentPlayer = 0;
int turn = 0;
while (!quit) {
System.out.println("Player " + (currentPlayer + 1) + "'s turn (" + players[currentPlayer] + ")");
makeBoard(board);
int move;
// allows player to move when playing against pc or when playing against other player
if ((gameMode == 2 && currentPlayer == 1) || gameMode == 1) {
move = scanner.nextInt() - 1;
scanner.nextLine();
// checks if move is valid
if (move < 0 || move >= board.length || !board[move].equals(String.valueOf(move + 1))) {
System.out.println("Invalid move, try again.");
continue;
}
} else {
// computer moves if game mode is against player
move = computerMove(board, random);
}
// counts turns
board[move] = players[currentPlayer];
turn++;
// checks if game is won
if (checkWin(board, players[currentPlayer])) {
System.out.println("Player " + (currentPlayer + 1) + " wins!");
quit = true;
} else if (turn == 9) {
System.out.println("It's a tie!");
quit = true;
}
// checks which player is playing
currentPlayer = (currentPlayer + 1) % 2;
}
scanner.close();
}
// computer AI
private int computerMove(String[] board, Random random) {
int emptyCellCount = 0;
// counts number of empty cells
for (String cell : board) {
if (!cell.equals(PLAYER_X) && !cell.equals(PLAYER_O)) {
emptyCellCount++;
}
}
// sets valid moves
int[] availableMoves = new int[emptyCellCount];
int index = 0;
// creates id for each available move
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
if (!board[i].equals(PLAYER_X) && !board[i].equals(PLAYER_O)) {
availableMoves[index++] = i;
}
}
// picks random move based on id number of valid cells
return availableMoves[random.nextInt(emptyCellCount)];
}
// makes the board using iteration
private void makeBoard(String[] board) {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i += 3) {
System.out.println(board[i] + " | " + board[i + 1] + " | " + board[i + 2]);
}
}
// using arrays to check win patterns
// signature boolean sends whether win patterns are complete
private boolean checkWin(String[] board, String player) {
int[][] winPatterns = {
{0, 1, 2}, {3, 4, 5}, {6, 7, 8}, // rows
{0, 3, 6}, {1, 4, 7}, {2, 5, 8}, // columns
{0, 4, 8}, {2, 4, 6} // diagonals
};
// returns if win pattern is chosen
for (int[] pattern : winPatterns) {
if (board[pattern[0]].equals(player) && board[pattern[1]].equals(player) && board[pattern[2]].equals(player)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConsoleGame game = new ConsoleGame();
game.start();
}
}
ConsoleGame.main(null)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
| Welcome to the Console Game!
�[38;5;141m___________________________
|~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~|
|�[0m Menu! �[38;5;141m|
|~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~|
| 0 - Exit |
| 1 - Rock Paper Scissors |
| 2 - Higher or Lower |
| 3 - Tic Tac Toe |
|_________________________| �[0m
Choose an option.
1:
Choose: 1 - Rock, 2 - Paper, 3 - Scissors
Computer: Scissors
Player: Scissors
Tie
�[0m
�[38;5;141m___________________________
|~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~|
|�[0m Menu! �[38;5;141m|
|~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~|
| 0 - Exit |
| 1 - Rock Paper Scissors |
| 2 - Higher or Lower |
| 3 - Tic Tac Toe |
|_________________________| �[0m
Choose an option.
2:
What number am I thinking of (1-10)?
Guess: 5
higher
Guess: 7
Correct!
�[0m
�[38;5;141m___________________________
|~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~|
|�[0m Menu! �[38;5;141m|
|~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~|
| 0 - Exit |
| 1 - Rock Paper Scissors |
| 2 - Higher or Lower |
| 3 - Tic Tac Toe |
|_________________________| �[0m
Choose an option.
3:
Tic Tac Toe
Choose game mode:
1. Play against player
2. Play against computer
Player 1's turn (X)
1 | 2 | 3
4 | 5 | 6
7 | 8 | 9
Player 2's turn (O)
1 | 2 | 3
4 | 5 | 6
7 | 8 | X
Player 1's turn (X)
1 | 2 | O
4 | 5 | 6
7 | 8 | X
Player 2's turn (O)
1 | 2 | O
4 | 5 | 6
7 | X | X
Player 1's turn (X)
1 | 2 | O
4 | 5 | 6
O | X | X
Player 2's turn (O)
1 | X | O
4 | 5 | 6
O | X | X
Player 2 wins!
�[0m
�[38;5;141m___________________________
|~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~|
|�[0m Menu! �[38;5;141m|
|~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~|
| 0 - Exit |
| 1 - Rock Paper Scissors |
| 2 - Higher or Lower |
| 3 - Tic Tac Toe |
|_________________________| �[0m
Choose an option.
0:
Goodbye, World!
|