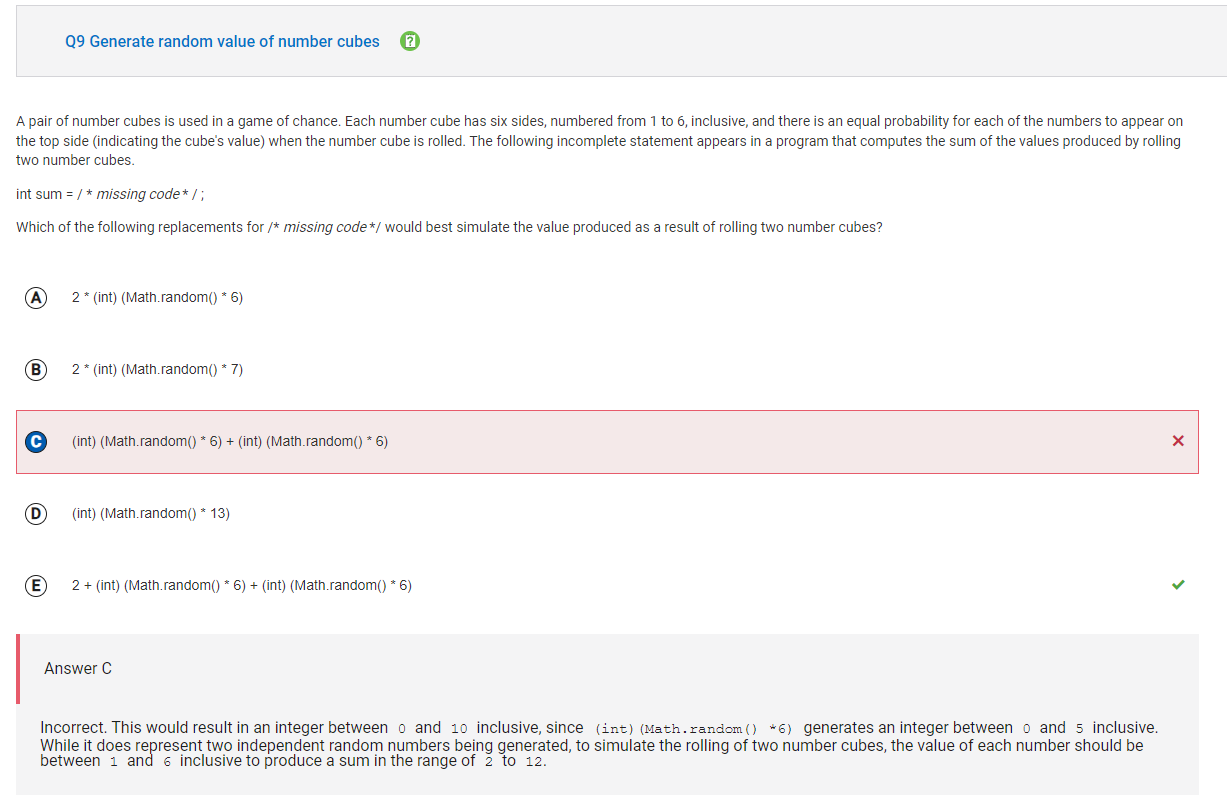
Q9 Generate random value of number cubes
The call Math.random() will produce a double between 0 and 1, not including 1. To generate a random number in the range of 1 to 6, the call Math.random() needs to be multiplied by the number of integers you want to generate, in this case 6, giving us Math.random() * 6. This will result in a double between 0 and 6, not including 6. If we type cast this to an int, as in (int)(Math.random() * 6), the result will be an integer between 0 and 5 inclusive. Adding 1 will adjust the range to 1 to 6 inclusive, as in (int)(Math.random() * 6) + 1. This expression will simulate the rolling of one number cube. Since each roll is independent, to simulate rolling two number cubes, we need to use this expression twice which simplifies to 2 + (int)(Math.random() * 6) + (int)(Math.random() * 6).
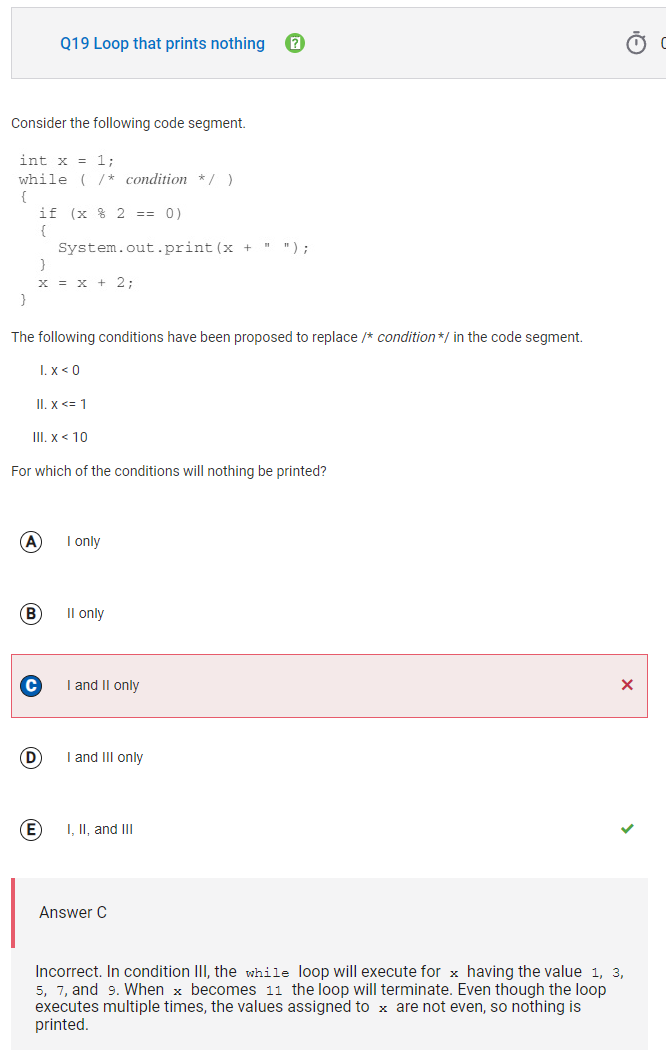
Q19 Loop that prints nothing
In condition I, the while loop will not execute, since 1, the value of x, is not less than 0, so nothing will be printed. In condition II, the while loop will execute one time, since 1, the value of x is less than or equal to 1, however, 1 is not even, so nothing will be printed. The value of x will then be incremented to 3, which is not less than or equal to 1, and the loop will terminate. In condition III, the while loop will execute for x having the value 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9. When x becomes 11 the loop will terminate. Even though the loop executes multiple times, the values assigned to x are not even, so nothing is printed.
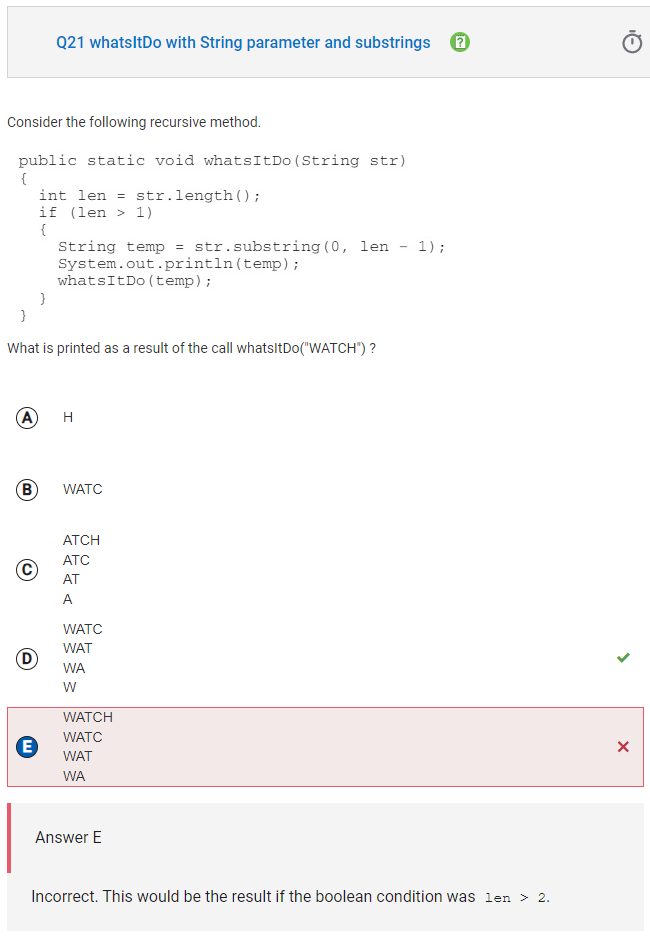
Q21 whatsItDo with String parameter and substrings
During each recursive call to whatsItDo, temp is assigned a substring of the parameter that excludes the last character, then prints this to the screen and calls whatsItDo with this substring. For the first recursive call, whatsItDo(“WATCH”) will print WATC and call whatsItDo(“WATC”). The call whatsItDo(“WATC”) will print WAT and call whatsItDo(“WAT”). The call whatsItDo(“WAT”) will print WA and call whatsItDo(“WA”). The call whatsItDo(“WA”) will print W and call whatsItDo(“W”). Since the length of string “W” is not greater than 1, the recursive method is complete.
Q29 what method with int parameter
Each recursive call is made with the value num / 10. The expression num / 10 uses integer division and evaluates to an integer that is num with the right most digit removed. For example, 258 / 10 = 25. Each time the recursive call is made, what is returned is 1 plus the result of the recursive call. For example, what(258) = 1 + what(25) and what(25) = 1 + what(2) and what(2) = 1. Therefore what(258) = 1 + 1 + 1 or 3, which is the number of digits in 258.
Q31 X and O board
The first set of nested for loops sets each element in board to “O”. The next for loop starts val at 0 and increments by 1 until val is 4, when val is 5 the loop terminates. When val is even, board is not updated, so nothing happens when val is 0. When val is 1, row is assigned 1 and col is assigned 0. The boolean condition in the while loop is true, so board[1][0] is assigned “X”. Then col is incremented to 1 and row is decremented to 0 and board[0][1] is assigned “X”. Then col is incremented to 2 and row is decremented to -1 and the while loop terminates. When val is 2, nothing changes about board. When val is 3, row is assigned 3 and col is assigned 0. The boolean condition in the while loop is true, so board[3][0] is assigned “X”. Then col is incremented to 1 and row is decremented to 2 and board[2][1] is assigned “X”. Then col is incremented to 2 and row is decremented to 1 and board[1][2] is assigned “X”. Then col is incremented to 3 and row is decremented to 0 and board[0][3] is assigned “X”. Finally, col is incremented to 4 and row is decremented to -1 and the while loop terminates. When val is 4, nothing changes about board.